IDDSI Swallowing Guidelines
IDDSI Swallowing Guidelines was written by dietetic intern Danea Albadri & reviewed/edited/updated by Katie Dodd, MS, RDN, CSG, LD, FAND.
Many people have difficulty swallowing and require specific diet modifications known as dysphagia diets. Traditionally, the standards for dysphagia diets, have varied in different countries across the globe. IDDSI (International Dysphagia Diet Standardization Initiative) is a global initiative to help create set standards for the dysphagia diet.
The IDDSI Framework provides consistent terminology and standards for food textures and liquid thickness for individuals with swallowing difficulties. Therefore, this framework sets a standard to define modified diets across the world and promotes swallowing safety.
What is IDDSI?
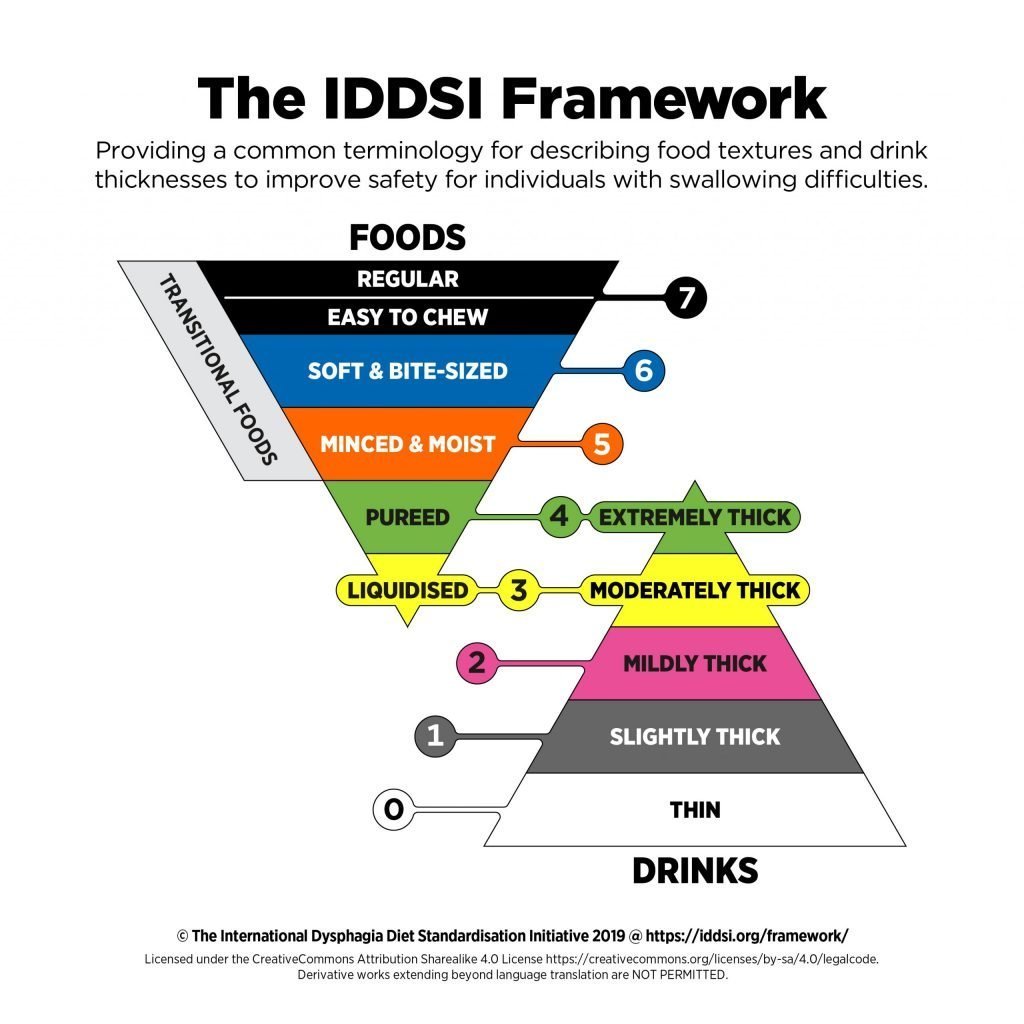
The IDDSI Framework contains a range of eight levels from 0 to 7. It specifies a terminology for drinks and food thicknesses. Drinks are segregated from level 0 to Level 4, while Levels 3 to 7 are used for measuring food. Of note, levels 3 and 4 overlap between food and drinks. IDDSI has specific tests to evaluate each level.
Dysphagia and Problems Swallowing
Dysphagia (difficulty swallowing) affects 8% of the world population. This accounts to around 590 million people around the globe. Thickened drinks and texture-modified foods generally help in decreasing the risks of aspiration and choking.
Levels of IDDSI
As stated, IDDSI has eight levels from 0 to 7. Levels 0 to 4 are defined for drinks, while food is defined under 3 to 7 levels. Of note, both levels 3 and 4 share similar characteristics and that’s why its both connected between drink and food levels.
Below is a description of each level. Each level has an associated label, number, and color. Levels 3 &4 have different labels for foods and drinks.
- Level 7: REGULAR/ EASY TO CHEW- regular & easy chew food items which are everyday food.
- Level 6: SOFT & BITE-SIZED- bite-sized & soft food which can be eaten with spoon, chopsticks, or fork.
- Level 5: MINCED & MOIST- moist & minced food, has lumps easily squashed with the tongue.
- Level 4: PUREED/ EXTREMELY THICK- pureed diet which doesn’t require chewing at all.
- Level 3: LIQUIDIZED/ MODERATELY THICK- liquidized food with no lumps or fiber.
- Level 2: MILDLY THICK- flows off a spoon and require a mild effort than water.
- Level 1: SLIGHTLY THICK- thicker than water and require a tiny more effort than water.
- Level 0: THIN- fast flow like water.
Then there are transitional foods in levels 5-7 that change its texture from firm solid when moistening with saliva or water. An example of a transitional food is ice-cream. It’s solid when eating, but quickly transitions to a liquid when eaten.
Below is the visual image of the IDDSI Framework from www.iddsi.org:
Here is another look at the levels breaking them down by foods and drinks:
Drinks level 0-4
Levels 0 to 4 defines standards for drinks:
- 0 – Thin
- 1 – Slightly Thick
- 2 – Mildly Thick
- 3 – Moderately Thick
- 4 – Extremely Thick
Food level 3-7:
Levels 3 to 7 defines standards for foods:
- 3 – Liquidized
- 4 – Pureed
- 5 – Minced and Moist
- 6 – Soft and bite-sized
- 7 – Regular/ Easy to Chew
While level 5 to 7 has foods called as transitional foods which changes food structure when water or heat applied and will not gain its original structure.
Testing Methods
Testing is the heart of IDDSI. It is how you confirm that the food and drinks prepared match the prescribed level.
IDDSI testing methods include:
- Fork Drip Test
- Chopstick Test
- Spoon Tilt Test
- Finger Test,
- Fork and Spoon Pressure Test
Drink Testing Method (flow test)
IDDSI uses the flow test for evaluating liquidized foods and drinks.
This test requires a 10 ml syringe. It is easy to use and simple. You can view the details here.
To conduct the flow test, fill the syringe to the 10 ml mark while using a finger to block the flow. Next you will remove your finger and allow the liquid to drain out for 10 seconds. After the 10 seconds put your finger back to block the flow. Finally, check the syringe to see how many ml are left. This will tell you the IDDSI level for the liquid.
IDDSI Level based on how much liquid is left in 10 ml syringe after 10 seconds of flow:
- 0: less than 1 ml fluid left
- 1: 1-4 ml fluid left
- 2: 4-8 ml fluid left
- 3: 8-10 ml fluid left
- 4: All 10 ml of fluid left
Food Testing Method (food test)
IDDSI uses following food testing methods for texture modified foods:
- Spoon Tilt Test – verifies cohesiveness (holding ability) and adhesiveness (stickiness) of food.
- Fork Drip Test – checks the cohesiveness and thickness in Levels 3 to 5 foods.
- Fork & Spoon Pressure Test – checks the hardness or firmness of food in Levels 4 to 7.
- Chopstick Test – Chopsticks used as a replacement of forks.
- Finger Test – This test has merged in recognition and might also be the most reachable process in some countries.
Implementing in the Workplace
In the United States many facilities are still using the National Dysphagia Diet (NDD). Others are actively transitioning from NDD to IDDSI. When it comes to implementing IDDSI in the workplace it is important to provide education to all staff involved in food preparation and serving.
Posting the IDDSI Framework in work areas may be helpful. It is important not to modify any of the IDDSI framework diagrams or descriptors. In other words, consistency is key for IDDSI.
IDDSI recommends using the Monitor- Aware- Prepare- Adopt method which is outline on their website. Building awareness, figuring out what needs to be in place, starting, and continually monitoring is important.
Manufacturer Guidelines
Be aware that manufacturer’s guideline for thickening agents leads to inconsistency between the prescribed consistencies and outcomes. When using specific products for thickening food and drinks, refer to the IDDSI standards and utilize recommended testing methods to ensure the appropriate levels are met.
IDDSI App
 IDDSI resources are available online and can be utilized for professional and personal use without prior permission. There are a ton of handouts and training materials.
IDDSI resources are available online and can be utilized for professional and personal use without prior permission. There are a ton of handouts and training materials.
There is also a helpful app available on both the android Play Store and Apple App Store. Search for “IDDSI app” in either store.
This app can easily be downloaded and utilized by the caregivers and other staff who prepare foods.
Additionally, the app contains handy tips which can be helpful for caregivers.
Conclusion
The IDDSI framework delivers common standardized definitions and terminologies for thickened liquids and texture-modified foods. It is aimed at improving patient care and safety for those with dysphagia. The key to implementing IDDSI is learning about the levels and how to appropriately test foods. Above all, education to all staff with follow-up is of the utmost important.
Also be sure to use the amazing resources provided on the IDDSI website to get started!
References
- https://www.asha.org/slp/healthcare/international-dysphagia-diet-standardisation-initiative/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29052849/
- https://ftp.iddsi.org/Documents/Testing_Methods_IDDSI_Framework_Final_31_July2019.pdf
