Oat milk vs soy milk have become popular dairy alternatives in recent years. Many people choose them for health reasons, ethical concerns, or taste preferences. But which one is better?
Both oat milk and soy milk offer unique nutritional benefits, but soy milk generally has more protein and fewer calories. Oat milk provides more riboflavin than cow’s milk, while soy milk is a good source of essential amino acids.
The choice between the two often comes down to personal taste, dietary needs, and environmental concerns.
We’ll compare these plant-based milks in terms of nutrition, health impacts, and environmental factors. This information will help you make an informed decision about which milk alternative might be best for you.
Table of Contents:
- Nutritional Comparison of Oat Milk vs Soy Milk
- Oat Milk vs Soy Milk: Health Considerations
- Sensory Experience: Flavor and Texture of Oat Milk vs Soy Milk
- Environmental and Ethical Considerations: Comparing Oat Milk vs Soy Milk
- What About Almond Milk?
- Oat Milk vs Soy Milk Conclusion
Nutritional Comparison of Oat Milk vs Soy Milk
Oat milk and soy milk have different nutritional profiles. Let’s look at their key nutrients to help you choose the best option for your needs!
Protein Content
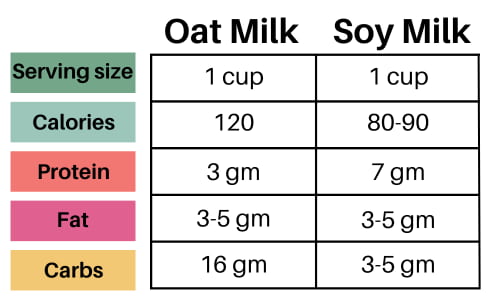
Soy milk is a protein powerhouse. It contains about 7 grams of protein per cup, similar to cow’s milk. This makes it great for muscle repair and growth.
Oat milk has less protein, with only about 3 grams per cup. If you need more protein in your diet, then soy milk might be the better choice.
Vitamin and Mineral Fortification
Both oat and soy milk are often fortified with vitamins and minerals. This means extra nutrients are added to make them more nutritious.
Many brands add calcium, vitamin D, and vitamin B12 to their plant milks. These nutrients are important for bone health and energy.
Soy milk naturally contains some minerals, while oat milk may need more fortification to match soy milk’s nutrient content.
Caloric and Fat Comparison
Oat milk tends to have more calories than soy milk. A cup of oat milk usually has about 120 calories.
Soy milk has fewer calories, with about 80-90 per cup. This makes soy milk a better option if you’re watching your calorie intake.
Fat content varies between brands. Most oat and soy milks have 3–5 grams of fat per cup. The type of fat matters too. Both contain mostly healthy unsaturated fats.
Carbohydrates and Fiber
Oat milk is higher in carbs. It has about 16 grams of carbs per cup. This includes some fiber, which is good for digestion.
Soy milk has fewer carbs, usually 3–5 grams per cup (though flavored versions can increase carbs to as much as 12–15 grams per cup). It also has some fiber, but less than oat milk.
The sugar content in oat milk can be higher, especially in flavored versions. Always check the label for added sugars.
Oat milk’s higher carbohydrate content makes it a good energy source. But if you’re limiting carbs, then soy milk might be a better choice.
If you’re trying to decide between oat and soy milk, these tips might help.
- Soy milk is a good choice if you want more protein, especially if you don’t eat meat.
- Oat milk is a better option if you’re looking to improve your heart health or want a milk that’s easy on your stomach and high in fiber.
Oat Milk vs Soy Milk: Health Considerations
Oat milk and soy milk offer different health benefits and potential concerns. Let’s explore their impact on allergies, chronic conditions, and overall well-being.
Allergies and Intolerances
Soy milk is unsuitable for people with soy allergies. It’s a common allergen that can cause reactions like hives, itching, and difficulty breathing. Oat milk is generally safe for those with soy allergies.
Oat milk may contain gluten if not certified gluten-free. This makes it problematic for people with celiac disease or who have a gluten sensitivity.
However, both oat and soy milk are lactose-free alternatives to cow’s milk. This makes them great choices for those who are lactose intolerant.
Impact on Chronic Health Conditions
Soy milk contains isoflavones, which may help lower cholesterol levels. (1) This can be beneficial for heart health and reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Oat milk is naturally low in saturated fat and contains beta-glucans. These fibers can help manage blood sugar levels, making it a good option for people with diabetes.
Soy milk’s protein content may aid in weight management, as it can help you feel fuller for longer.
Health Benefits of Oat Milk vs Soy Milk
As we mentioned above, soy milk is high in protein, providing all essential amino acids. This makes it valuable for muscle building and repair, especially in vegan diets.
Oat milk is rich in fiber, supporting digestive health and promoting feelings of fullness.
And again, both milks are often fortified with vitamins and minerals. This includes calcium and vitamin D for bone health, and vitamin B12 for nerve function.
Potential Downsides
Some worry about phytoestrogens in soy milk affecting hormone levels. However, research shows moderate consumption is safe for most people.
Oat milk is higher in carbohydrates and calories compared to soy milk. This may be a concern for those watching their calorie intake.
Some oat and soy milks contain added sugars (especially when these milks are flavored). It’s important to check the nutrition labels and choose unsweetened versions if you are watching your sugar and/or carbohydrate intake.
Sensory Experience: Flavor and Texture of Oat Milk vs Soy Milk
Oat milk vs soy milk offer different taste experiences and textures. These differences affect how you might enjoy them and use them in recipes.
Taste Profiles
Oat milk has a mild, slightly sweet flavor. It tastes a bit like oatmeal. Many people find it pleasant and easy to drink. Soy milk has a more distinct taste. It is slightly nutty or “bean-y.” Some people don’t mind this flavor, while others may need time to get used to it.
Both milks come in plain and flavored versions, such as vanilla and chocolate. Flavored versions tend to be sweeter and can help mask the base taste.
As an aside, we’ve noticed that oat milk often works better in coffee. It doesn’t curdle and has a neutral taste that blends well!
Consistency and Uses in Recipes
Oat milk is known for its creamy texture. It’s thick and smooth, making it great for lattes and baked goods. Soy milk is thinner but still creamy. It works well in both sweet and savory dishes.
In cooking, soy milk is versatile as it can replace dairy milk in most recipes. Oat milk shines in baking and hot drinks, and it creates a nice foam for cappuccinos.
We find that soy milk works better for making vegan yogurt. It has more protein, which helps create a thicker consistency, and makes it more nutrient-dense.
Both milks can be used in smoothies, cereals, and sauces. The choice often comes down to personal taste preference and dietary needs.

Environmental and Ethical Considerations: Comparing Oat Milk vs Soy Milk
Oat milk and soy milk have different impacts on the environment and raise various ethical concerns. We’ll explore how these plant-based milks compare in terms of sustainability, farming practices, and animal welfare.
Environmental Impact
Plant-based milks like oat and soy are more environmentally friendly than cow’s milk. They produce fewer greenhouse gases and use less land and water. Oat milk has an especially low carbon footprint compared to other alternatives.
Soy milk requires more land than oat milk, but less land than cow’s milk.
Cow’s milk uses about 9 square meters of land per liter of milk produced. While soy milk uses about 0.7 square meters of land per liter produced and oat milk uses even less at 0.8 square meters per liter.
Dairy farming also contributes to deforestation in some regions – as more land is needed to produce the milk.
Water use is another important environmental factor to consider. Oat and soy milk production requires significantly less water than dairy milk.
Organic Options and Pesticides
Both oat and soy milk can be produced organically. Organic farming restricts the use of synthetic pesticides and fertilizers. This can be better for soil health and biodiversity.
Non-organic oats and soybeans may be treated with pesticides. Some consumers worry about pesticide residues in the final products. Choosing organic options can address these concerns.
Organic farming practices can also benefit wildlife and ecosystems. They often promote greater biodiversity on farms, which can help create habitats for insects and birds.
We should note that organic doesn’t always mean pesticide-free. Organic farmers can use certain approved pesticides when needed.
Sustainable Farming Practices
Oat and soy farming can use sustainable methods. Crop rotation helps maintain soil health and reduce pest problems. This can decrease the need for chemical inputs as well.
Cover cropping is another eco-friendly practice. It prevents soil erosion and adds nutrients naturally. Many oat and soy farmers use this technique.
No-till farming is gaining popularity for both crops. It helps preserve soil structure and reduces carbon emissions. (This method keeps more carbon in the soil instead of releasing it into the atmosphere).
Additionally, water-efficient irrigation systems can further reduce environmental impact. Drip irrigation and precision agriculture techniques help conserve water in dry regions.
Animal Welfare and Plant-based Alternatives
Plant-based milks like oat and soy offer ethical alternatives to dairy, as they don’t involve animal farming. These address concerns about animal welfare in the dairy industry.
Dairy cows may face issues like confined living conditions and separation from calves, while plant-based milks avoid these ethical dilemmas entirely.
Choosing oat or soy milk supports a more vegetarian or vegan lifestyle as well. This can reduce overall demand for animal products and their associated environmental impacts.
Plant-based options also cater to those with lactose intolerance or milk allergies. They provide nutritious alternatives without relying on animal sources.
What About Almond Milk?
Almond milk is another popular plant-based milk option. We find it has a mild, nutty flavor that many people enjoy.
When comparing oat milk vs almond milk vs soy milk, there are some key differences to note:
- Calories: Almond milk is typically lower in calories than both oat and soy milk.
- Protein: Soy milk has the highest protein content, followed by oat milk, with almond milk having the least.
- Fat: Almond milk is often lower in fat than soy milk, but may have similar fat content to oat milk.
Almond milk shines in its vitamin E content. It’s naturally rich in this antioxidant, which supports skin health.
One advantage of almond milk is its versatility. We can use it in coffee, smoothies, and baking without significantly altering flavors.
Almond milk vs soy milk: compared to soy milk, almond milk has a milder taste that some find more agreeable. This can make it a better choice for use in cereals or cooking.
Nutritionally, almond milk is often fortified with calcium and vitamin D, similar to oat and soy milk. However, it naturally contains less protein and other nutrients than its counterparts.
Oat Milk vs Soy Milk Conclusion
Oat milk and soy milk are both popular plant-based milk alternatives. Each has its own unique qualities and benefits.
Soy milk contains more protein than oat milk. It’s a good choice for those looking to increase their protein intake. Oat milk is higher in carbohydrates and fiber. This makes it a satisfying option that can help keep you feeling full.
Both milks can be fortified with vitamins and minerals, which helps them provide similar nutrients to cow’s milk. Taste and texture differ between the two. Oat milk tends to be creamier, while soy milk has a distinct flavor that some prefer more than others.
We recommend trying both to see which you like best! Your choice may depend on nutritional needs, taste preferences, and dietary restrictions.
Remember, both can be healthier alternatives to cow’s milk for those who are lactose intolerant or those following a plant-based diet.
