Easy HbA1c Conversion Chart [Free PDF]
“Easy HbA1c Conversion Chart [Free PDF]” was written by Irene Mejía & edited/reviewed by Aly Bouzek, MS, RDN. Irene is a dietetic intern at Larkin University.
If you are someone who has to assess and control glucose levels on a regular basis, then it’s very likely that you use a glucometer that gives you results with a unit such as mg/dL or mmol/L.
But your doctor may have also indicated for you to get some blood work done. When you receive the results, you notice that there’s a test called HbA1c with a percentage (%) sign next to it.
Now, you may be wondering what HbA1c is and what it means for your blood sugar levels? You’re not alone!
In this blog post, we’ll explain everything you need to know about glucose tests, HbA1c tests, how to convert one to the other, and also the new guidelines that are being used by doctors around the world.
Follow along below!
Blood Glucose Tests
How Are They Done?
As the name indicates, blood glucose tests are done by assessing the glucose (sugar) levels in your blood at that specific moment in time (at the time of the test).
There are two ways you can do a blood test:
- Laboratory: your doctor indicated to go to a laboratory to get your blood drawn. You usually receive the results within a few days or your doctor discusses them with you on your next visit.
- Glucometer: if you have been diagnosed with pre-diabetes or diabetes, you may be familiar with glucometers.
With the help of a lancing device (a device with a small needle) you can make a tiny prick in your skin to obtain a few drops of blood.
Then, the glucometer can determine the glucose level in your small blood sample.
What Time of the Day Are Blood Tests Taken?
This will depend on what your doctor indicates. For example, your doctor may want to know your fasting blood glucose levels. This measures your blood sugar after an overnight of no eating (also known as “fasting”).
Your physician may also be interested in a random blood glucose test. This measures your blood sugar at the exact moment that you’re tested. You can take this test at any time and don’t need to fast first.
Blood Glucose Levels – Units & Guidelines
The unit of glucose monitors or blood tests varies depending on the country.
The United States uses mg/dL and Europe uses mmol/L.
The following are the current guidelines in the United States. The units are in mg/dL: (1)
| Result* | Fasting Blood Sugar Test | R2andom Blood Sugar Test |
| Diabetes | 126 mg/dL or above | 200 mg/dL or above |
| Prediabetes | 100 – 125 mg/dL | N/A |
| Normal | 99 mg/dL or below | N/A |
The following are the current guidelines for countries using the unit mmol/L: (2)
| Result* | Fasting Blood Sugar Test | Random Blood Sugar Test |
| Diabetes | 7 mmol/L or above | 11.1 mmol/L or above |
| Prediabetes | 5.6 to 6.9 mmol/L | N/A |
| Normal | 5.6 mmol/L or below | N/A |
Note: Oral glucose tolerance test results (which measures your blood sugar before and after you drink a liquid that contains glucose) are also given in these units.
HbA1c Test
Blood glucose tests indicate glucose levels at that specific moment in time, while the HbA1c test gives the average glucose levels of the past 3 months.
How Does it Work?
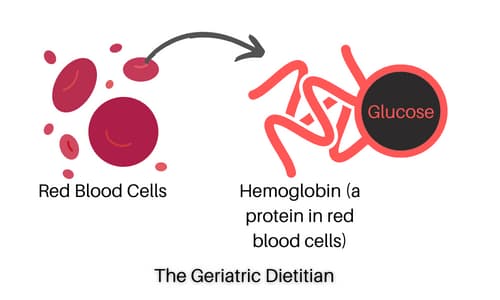
This test also relies on a protein called hemoglobin. Hemoglobin is a part of red blood cells that carries oxygen. (3)
Glucose sticks to hemoglobin. So, the more glucose (or sugar) that’s in your blood, the more it will stick to the hemoglobin.
The average lifespan of red blood cells is about 120 days (or about 3-4 months). So, this test can measure the average blood glucose level during the previous 2 to 3 months with the “modified” hemoglobin. (4)
Why is it Useful?
Similar to blood glucose tests, this test can help detect pre-diabetes or help to diagnose diabetes. Most importantly, it can tell how well a person with diabetes has been managing their blood sugar.
For example, someone with diabetes could have been controlling their diabetes almost perfectly in the past few months, but the day of getting a blood test done at a laboratory they maybe don’t follow their usual routine.
This could result in abnormal glucose levels at that time, but it does not mean that they haven’t been taking control over their blood sugar in the past few months.
HbA1c – Units & Guidelines
The unit for this test also varies depending on the country. In the United States the results are given as a percentage (%) and in Europe it is common to use mmol/mol.
(*Important: mmol/mol are not the same unit as blood glucose tests, which is mmol/L. They look similar as the ranges are very close, but they are not the same).
The current guidelines in the United States are: (3)
| Result* | HbA1c |
| Goal for someone managing diabetes | 7% or below |
| Diabetes diagnosis | 6.5% or above |
| Prediabetes | 5.7% to 6.4% |
| Normal | 5.6% or below |
The World Health Organization (WHO) suggests the following diagnostic guidelines for diabetes using the unit mmol/mol: (5)
| Result* | HbA1c |
| Diabetes diagnosis | 48 mmol/mol or over |
| Prediabetes identification | 42 – 47 mmol/mol |
| Normal | 41 mmol/mol or below |
eAG – The New Guidelines
As you learned from the previous sections, glucose tests and their results can be confusing and hard to understand.
Since HbA1c is expressed as either a percentage or mmol/mol, it is not something that intuitively relates to the glucose results obtained through a glucometer.
The good news is that a study affirmed the existence of a relationship between HbA1c and average blood glucose levels! (6) This means that it is possible to convert one to the other.
In other words, your physician can now report your HbA1c using the same units as your glucometer (mg/dL or mmol/L). But if that is not the case, then don’t worry, with the help of our conversion charts you will be able to easily do it yourself!
HbA1c Conversion Chart: United States
HbA1c Conversion Chart: United States – HbA1c (%) to eAG (mg/dL)

If you want a PDF of our HbA1c conversion chart, click here.
HbA1c Conversion Chart: Europe
HbA1c Conversion Chart: Europe – HbA1c (mmol/mol) to eAG (mmol/L)

If you want a PDF of our HbA1c conversion chart, click here.
Note: For this chart, the HbA1c levels were converted from % to mmol/mol (7) and then from mmol/mol to mmol/L. (8)
Bottom Line for HbA1c Conversion Chart
You can assess your glucose levels in different ways. If you want to know your glucose levels at this exact moment in time, then you’ll either use a glucometer or go to a laboratory to obtain a blood glucose test.
However, your physician may indicate a HbA1c test. This is a blood test that measures the average blood sugar levels over the past 3 months.
The problem is that blood glucose tests and the HbA1c tests have different units, and they can also vary depending on each country.
However, now you can convert your HbA1c to the units you commonly see in your glucometer. With the help of our conversion charts, you can now easily convert your HbA1c to glucose levels and vice versa.
Let us know in the comments below if this post helped you clarify all your questions about glucose tests and units!
Resources:
- Diabetes: Diabetes Tests. Center for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/basics/getting-tested.html.
- Diabetes. Mayo Clinic. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/diabetes/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20371451.
- Glycated Hemoglobin Test (A1c). Cleveland Clinic. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diagnostics/9731-glycated-hemoglobin-test-a1c.
- Freeman V. Glucose and hemoglobin A1C. Laboratory Medicine. 2014;45(1):e21-e24. https://academic.oup.com/labmed/article/45/1/e21/2657883.
- HbA1c Test for Diabetes. Diabetes.co.uk. https://www.diabetes.co.uk/hba1c-test.html.
- Average Glucose Flyer. American Diabetes Association. https://professional.diabetes.org/sites/professional.diabetes.org/files/media/average_glucose_flyer.pdf.
- HbA1c Units Conversion Chart. Diabetes.co.uk. https://www.diabetes.co.uk/downloads/files/HbA1c%20units%20DCCT%20to%20IFCC.pdf.
- Convert between NGSP, IFCC and eAG. National Glycohemoglobin Standardization Program. http://www.ngsp.org/convert1.asp.
